There are 8 planets in our Solar System. They are classified in 2 types:
i. Terrestrial Planets/Inner Planets
ii. Gas Giants/Outer planets/jovial plantes
Terrestrial planets include- Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
Gas Giants include-Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Comparison:
i. Terrestrial planets are mainly made of rocks whereas Gas giants are made of gases.
ii. Terrestrial planets are smaller in size.
iii. Terrestrial planets rotate slowly in their axis as compared to Gas giants.
iv. Terrestrial planets' revolution period is faster than Gas giants.
v. Terrestrial planets have no moon or less moon (max. 2 for mars).
vi. Terrestrial planets have thinner atmosphere.
vii. Terrestrial planets have no rings.
viii. Terrestrial planets have weaker magnetic field.
1. Mercury:
Smallest planet. It has no atmosphere. No Satellite. One part is always towards sun and another always dark. Dirunal temp. range is maximum. Two Spacecrafts that have visited Mercury are - Mariner 10 and Messenger.
2. Venus:
Brightest and hottest planet. Direction of rotation is from east to west. Rotational speed is slowest. No Satellite. Also called Sister planet of Earth.
3. Mars:
Also called Red Planet. Red color is due to presence of Iron Oxides. It has 2 Satellites- Deimos and Phobos. Deimos is the smallest satellite. Mariner Valley is one vast canyon across its equator. Nix Olympia is the highest mountain on Mars.

4. Jupiter:
Biggest planet. Fastest Rotational period. Its surface has a red spot which is a persistent anticyclonic storm. Most no. of natural Satellites (67). Some important ones are-Ganymede, Europa, Callisto. Ganymede is the biggest Satellite.

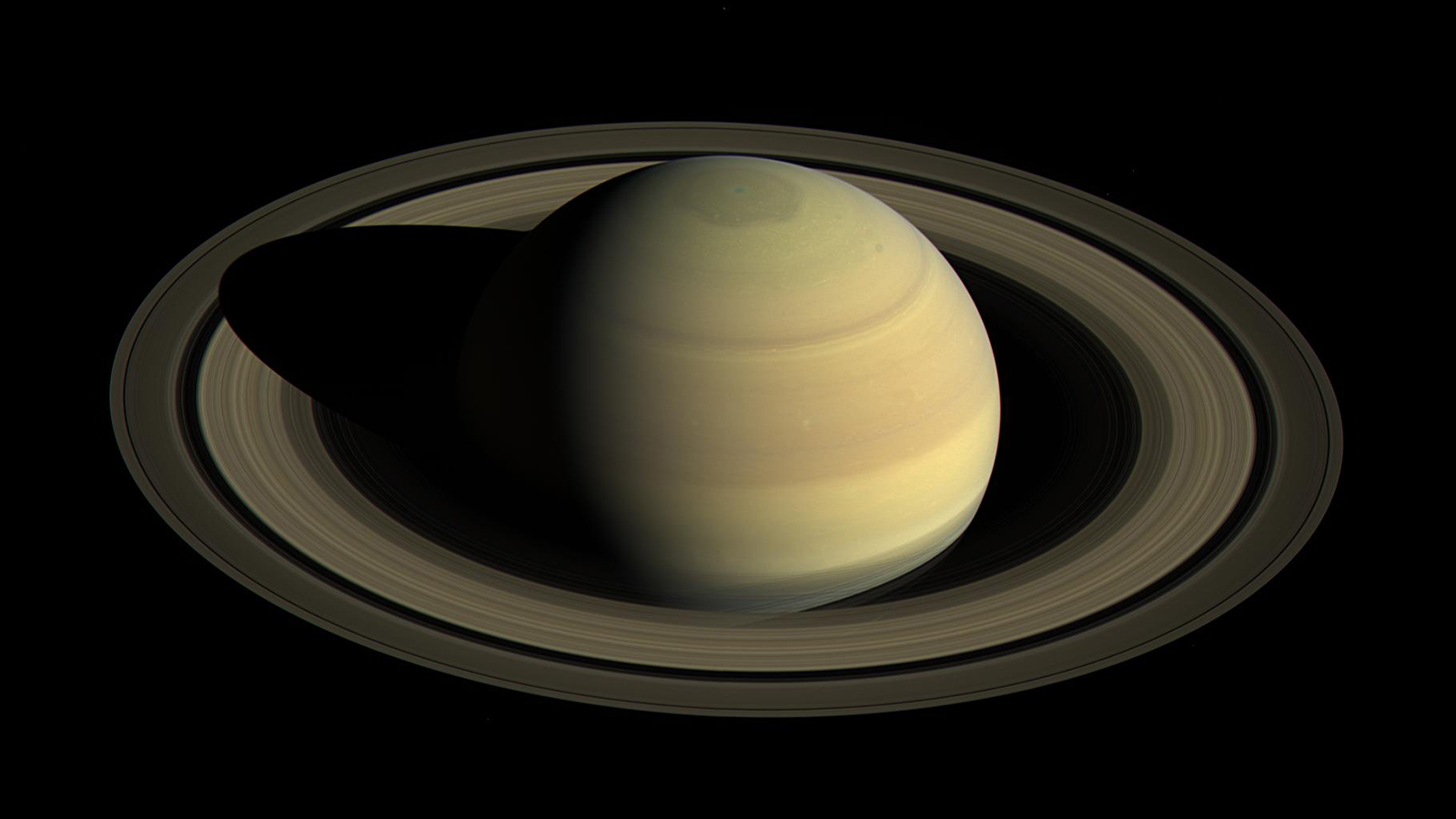
5. Saturn:
Surrounded by Shell of rings made of premordial dust and ice particles. Titan is its largest Satellite. Tethys and Phoebe are its other satellites. Phoebe Satellite is retrograde i.e. it orbits Saturn opposite to Saturn's rotation.
6. Uranus:
Also called green planet. Its spin axis is inclined by 98 degrees compared to its orbital plane. Rotation is East to West. Miranda and Ariel are important satellites.

7. Neptune:
Outermost planet. Blue in color due to presence of Methane and Ammonia. It has a Great dark spot due to presence of Anticyclonic Storm similar to Red spot in Jupiter. Coldest planet. Important satellites are - Triton, Nerid, Larrisa.
i. Terrestrial Planets/Inner Planets
ii. Gas Giants/Outer planets/jovial plantes
Terrestrial planets include- Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
Gas Giants include-Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Comparison:
i. Terrestrial planets are mainly made of rocks whereas Gas giants are made of gases.
ii. Terrestrial planets are smaller in size.
iii. Terrestrial planets rotate slowly in their axis as compared to Gas giants.
iv. Terrestrial planets' revolution period is faster than Gas giants.
v. Terrestrial planets have no moon or less moon (max. 2 for mars).
vi. Terrestrial planets have thinner atmosphere.
vii. Terrestrial planets have no rings.
viii. Terrestrial planets have weaker magnetic field.
1. Mercury:
Smallest planet. It has no atmosphere. No Satellite. One part is always towards sun and another always dark. Dirunal temp. range is maximum. Two Spacecrafts that have visited Mercury are - Mariner 10 and Messenger.
2. Venus:
Brightest and hottest planet. Direction of rotation is from east to west. Rotational speed is slowest. No Satellite. Also called Sister planet of Earth.
3. Mars:
Also called Red Planet. Red color is due to presence of Iron Oxides. It has 2 Satellites- Deimos and Phobos. Deimos is the smallest satellite. Mariner Valley is one vast canyon across its equator. Nix Olympia is the highest mountain on Mars.
4. Jupiter:
Biggest planet. Fastest Rotational period. Its surface has a red spot which is a persistent anticyclonic storm. Most no. of natural Satellites (67). Some important ones are-Ganymede, Europa, Callisto. Ganymede is the biggest Satellite.

5. Saturn:
Surrounded by Shell of rings made of premordial dust and ice particles. Titan is its largest Satellite. Tethys and Phoebe are its other satellites. Phoebe Satellite is retrograde i.e. it orbits Saturn opposite to Saturn's rotation.

6. Uranus:
Also called green planet. Its spin axis is inclined by 98 degrees compared to its orbital plane. Rotation is East to West. Miranda and Ariel are important satellites.

7. Neptune:
Outermost planet. Blue in color due to presence of Methane and Ammonia. It has a Great dark spot due to presence of Anticyclonic Storm similar to Red spot in Jupiter. Coldest planet. Important satellites are - Triton, Nerid, Larrisa.
Comments
Post a Comment